The Ankle Brachial Index (ABI) exam is the most simple and common test currently used to diagnose Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD). An Ankle Brachial Index (ABI) uses an ultrasound Doppler to assess the ratio of the highest systolic pressure at the arm to the systolic pressure at the ankle. Ankle Brachial Index studies are considered reimbursable when performed using a bidirectional Doppler with hard-copy output. You can read about how to perform a more thorough vascular exam in podiatry today.
Take a blood pressure reading at the arm
- Place a blood pressure cuff around the patient’s arm. Place ultrasound gel on the tip of the probe and apply the probe at a 45 to 60 degree angle over the brachial or radial artery.
- Wait for Doppler sounds to become stable. If your Doppler has an LCD display, watch the waveform on the display until it becomes rhythmic and stable.
- Inflate the cuff to 20 mmHg over pressure cessation. Then, slowly deflate the cuff until the first Doppler sound is heard.
- Record the systolic pressure when the first sound is heard and repeat the test on the other arm. Use the highest arm pressure to calculate the ABI to rule out subclavean steal syndrome.
Take a systolic pressure at the ankle
- Place a blood pressure cuff snugly above the patient’s ankle. Place ultrasound gel on the probe tip and apply the probe at a 45 to 60 degree angle over the posterior tibial or dorsalis pedis artery.
- Wait for Doppler sounds to become stable. If your Doppler has an LCD display, watch the waveform on the display until it becomes rhythmic and stable.
- Print the waveform for documentation
- Inflate the cuff to 20 mmHg over pressure cessation. Then, slowly deflate the cuff until the first Doppler sound is heard.
- Record the systolic pressure when the first sound is heard and repeat the test on the other leg.
Interpreting the Results Waveform Examples To calculate the ABI, divide the ankle pressure by the highest arm pressure 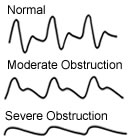
![]() Interpretation ¹ Greater than 1.30 = Noncompressible 0.91 – 1.30 = Normal 0.41 – 0.90 = Mild to Moderate PAD 0.00 – 0.40 = Severe PAD
Interpretation ¹ Greater than 1.30 = Noncompressible 0.91 – 1.30 = Normal 0.41 – 0.90 = Mild to Moderate PAD 0.00 – 0.40 = Severe PAD
